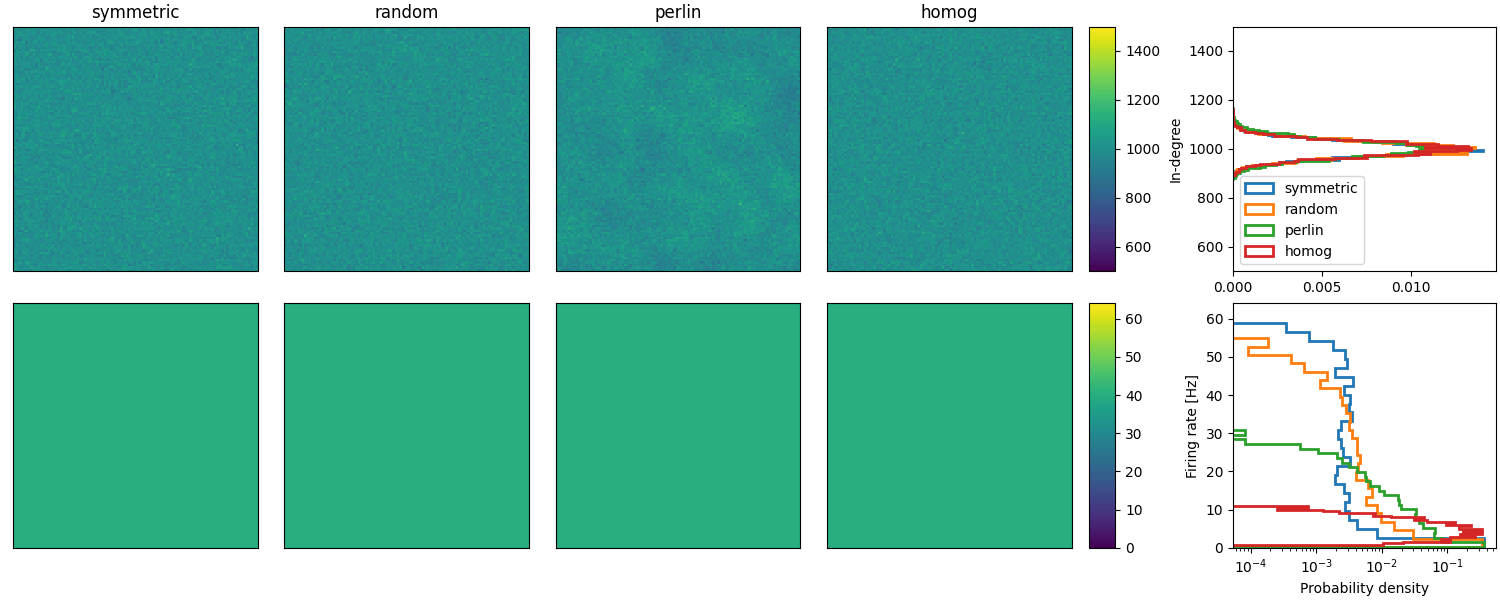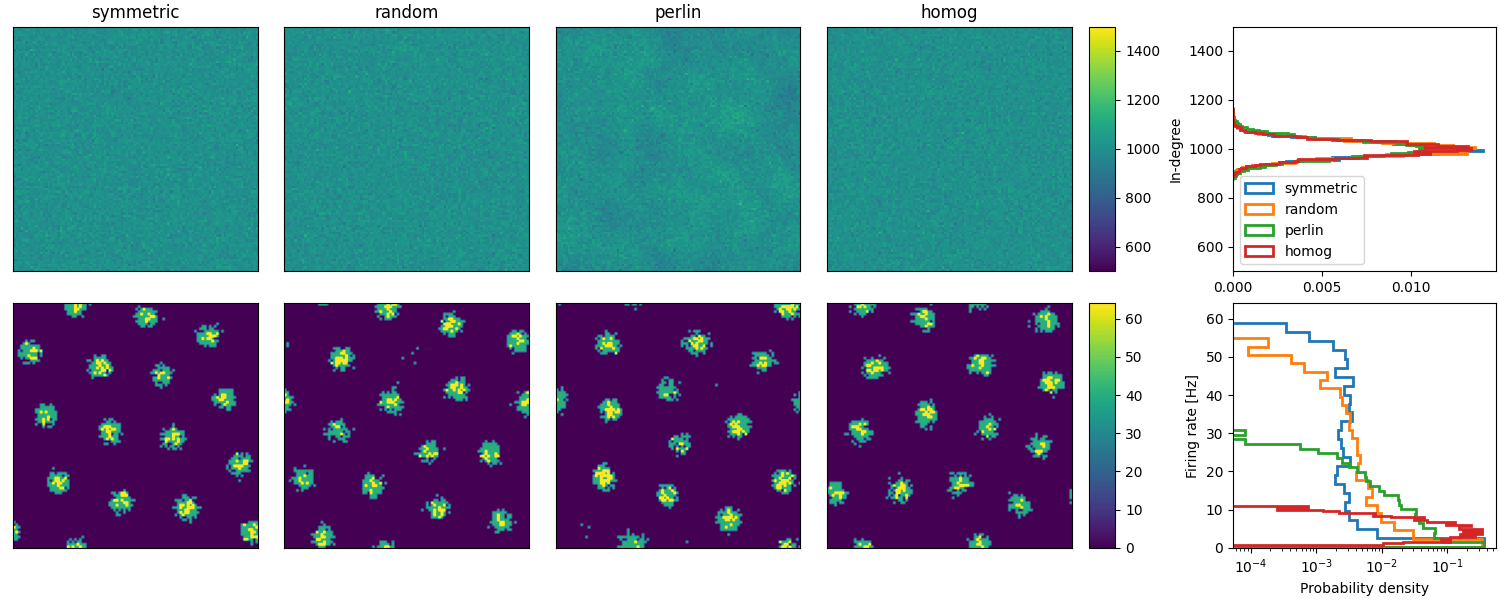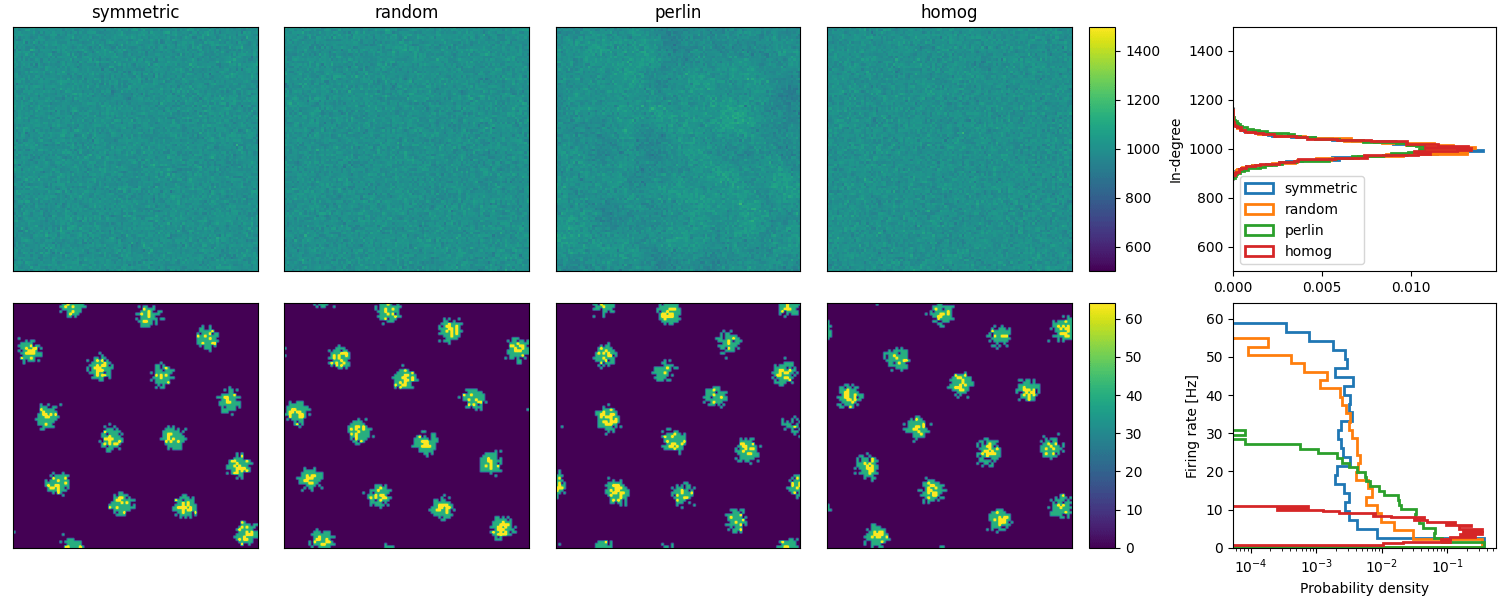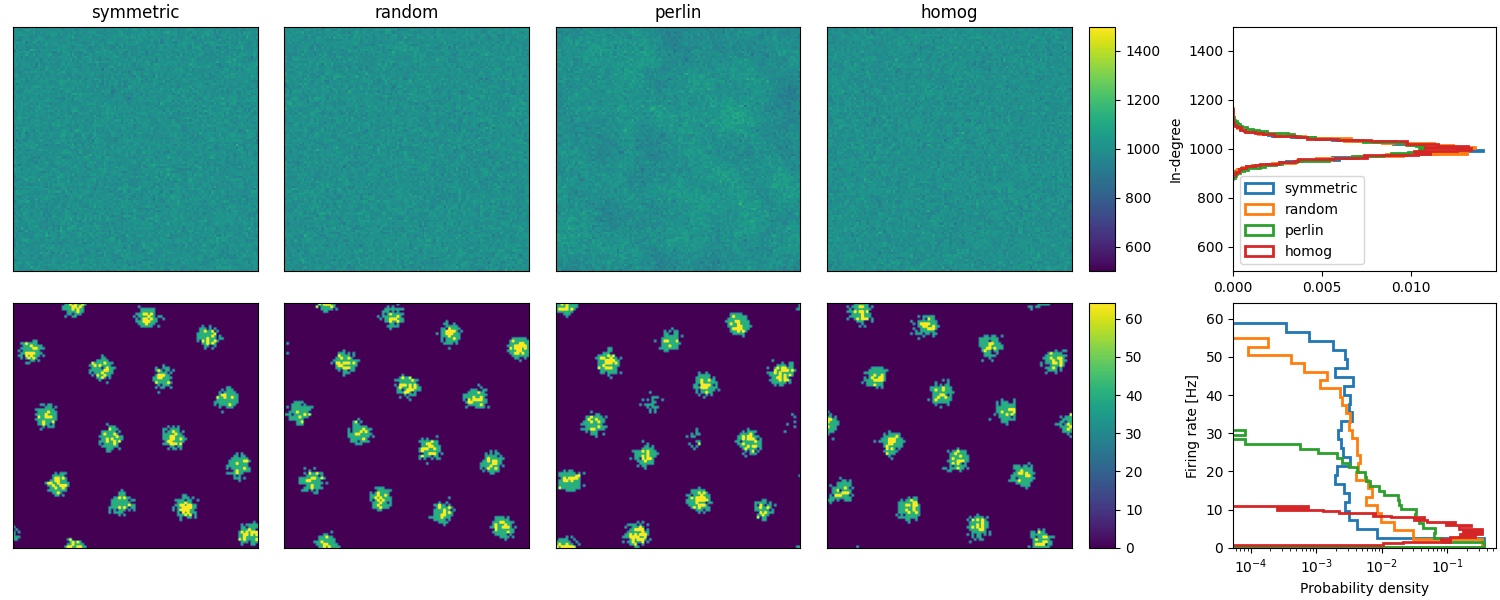
Example: Spreizer_et_al_2019
Reproduction of Fig. 2 (b and c) of Spreizer et al. 2019 in Brian:
Spreizer S, Aertsen A, Kumar A. From space to time: Spatial inhomogeneities lead to the emergence of spatiotemporal sequences in spiking neuronal networks. PLOS Computational Biology. 2019;15(10):e1007432. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007432
Requires the
noisepackage for setting up the Perlin landscape with freshly generated noise. Otherwise, the landscapes for different network sizes (scaled down by a factor of 1 to 5) can be loaded from the provided files.
This code was written by Arash Golmohammadi, 2022. Modified plotting code by Marcel Stimberg, 2023.
import os
import numpy as np
import brian2 as b2
from brian2.units import ms, pA, mV
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation
b2.seed(8)
def round_to_even(gs, scaler):
"""
rounds the network size to an even number.
"""
rounded = round(gs / scaler)
if rounded % 2:
rounded += 1
return int(rounded)
# ---------------- CONFIGURATIONS ---------------- #
# NETWORK TOPOLOGY
SCALE_DOWN = 5 # For faster computation I recommend running with SCALE_DOWN 2 or 3
GRID_SIZE = round_to_even(100, SCALE_DOWN)
NCONN = round_to_even(1000, SCALE_DOWN**2)
# CELL CONFIGS
THR, REF, RESET = -55 * mV, 2 * ms, -70 * mV
# PROFILE
THETA, KAPPA, GAP = 3 / SCALE_DOWN, 4, 3
# ANISOTROPY
R, SCALE = 1.0, 4 # perlin noise
PHI_H = np.pi / 6 # homog. angle
# WARMUP
DUR_WU, STD_WU = 500 * ms, 500 * pA
# BACKGROUND
MU, SIGMA = 700 * pA, 100 * pA
EQ_NRN = """
dv/dt = (E-v)/tau_m + (noise + I_syn)/C : volt (unless refractory)
I_syn : amp
noise = mu + sigma*sqrt(noise_dt)*xi_pop: amp
mu : amp (shared)
sigma : amp (shared)
noise_dt = 1*ms : second (shared)
C = 250*pF : farad (shared)
tau_m = 10*ms : second (shared)
E = -70*mV : volt (shared)
"""
EQ_SYN = f"""
dg/dt = (-g+h) / tau_s : 1 (clock-driven)
dh/dt = -h / tau_s : 1 (clock-driven)
I_syn_post = J*g : amp (summed)
J = -{SCALE_DOWN}*10*pA : amp (shared)
tau_s = 5*ms : second (shared)
"""
ON_PRE = "h += exp(1)" # to match NEST's normalization
# ---------------- UTILITIES ---------------- #
def coord2idx(coords, pop):
"""Converts array of coordinates to indices."""
coords = np.asarray(coords).reshape(-1, 2)
idxs = coords[:, 1] * GRID_SIZE + coords[:, 0]
return idxs
def idx2coord(idxs, pop):
"""Converts array of indices to coordinates"""
idxs = np.asarray(idxs)
y, x = np.divmod(idxs, GRID_SIZE)
coords = np.array([x, y]).T
return coords
def make_periodic(x, y, grid_size=GRID_SIZE):
x = x % GRID_SIZE
y = y % GRID_SIZE
return x, y
# ---------------- LANDSCAPE GENERATION ---------------- #
def landscape(anisotropy="perlin"):
"""Generates an angular bias for each neuron in the
network such that no angle is more likely than the
other. Yet, nearby bias angles may be correleted.
Note that this is a flattened array."""
if anisotropy == "perlin": # requires noise package
if os.path.exists(f"perlin{SCALE_DOWN}.npy"):
print("Loading perlin noise from file...")
phis = np.load(f"perlin{SCALE_DOWN}.npy")
else:
print("Generating perlin noise...")
from noise import pnoise2 as perlin
x = y = np.linspace(0, SCALE, GRID_SIZE)
phis = [[perlin(i, j, repeatx=SCALE, repeaty=SCALE) for j in y] for i in x]
phis = np.concatenate(phis)
phis = balance_landscape(phis)
phis -= phis.min()
phis *= 2 * np.pi / phis.max()
elif anisotropy == "homog":
phis = np.ones(GRID_SIZE**2) * PHI_H
else: # both random and symmetric have the same landscape
phis = np.random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi, size=GRID_SIZE**2)
return phis
def balance_landscape(array):
"""Equalizes the histogram."""
sorted_idx = np.argsort(array)
gs = int(np.sqrt(len(array)))
max_val = gs * 2
idx = int(len(array) // max_val)
for i, val in enumerate(range(max_val)):
array[sorted_idx[i * idx : (i + 1) * idx]] = val
return (array - gs) / gs
# ---------------- NETWORK SETUP ---------------- #
def setup_net(phis):
I = b2.NeuronGroup(
N=GRID_SIZE**2,
name="I",
model=EQ_NRN,
refractory=5 * ms,
threshold=f"v>{THR / mV}*mV",
reset=f"v={RESET / mV}*mV",
method="euler",
)
I.mu = MU
I.sigma = SIGMA
syn_II = b2.Synapses(
I, I, model=EQ_SYN, on_pre=ON_PRE, method="exact", name="syn_II"
)
for s_idx in range(len(I)):
rel_coords = draw_post(s_idx, phis[s_idx])
s_coord = idx2coord(s_idx, I) # check shape
x, y = (rel_coords + s_coord).T
x, y = make_periodic(x, y)
t_coords = np.array([x, y]).T.astype(int)
t_idxs = coord2idx(t_coords, I)
syn_II.connect(i=s_idx, j=t_idxs)
return I, syn_II
def draw_post(idx, phi):
alpha = np.random.uniform(-np.pi, np.pi, NCONN)
radius = np.concatenate(
[
-np.random.gamma(shape=KAPPA, scale=THETA, size=int(NCONN // 2)),
+np.random.gamma(shape=KAPPA, scale=THETA, size=NCONN - int(NCONN // 2)),
]
)
radius[radius < 0] -= GAP
radius[radius >= 0] += GAP
x, y = radius * np.cos(alpha), radius * np.sin(alpha)
x += R * np.cos(phi)
y += R * np.sin(phi)
eps = 1e-3
self_link = x**2 + y**2 < eps**2
x = x[~self_link]
y = y[~self_link]
coords = np.array([x, y]).T
return np.round(coords).astype(int)
def warmup(net):
net["I"].mu = 0 * pA
net["I"].sigma = STD_WU
net.run(DUR_WU / 2)
net["I"].mu = MU
net["I"].sigma = SIGMA
net.run(DUR_WU / 2)
def simulate(phis, dur=3000 * ms):
b2.start_scope()
I, syn_II = setup_net(phis)
mon = b2.SpikeMonitor(I, record=True)
net = b2.Network()
net.add(I)
net.add(syn_II)
net.add(mon)
warmup(net)
net.run(dur)
return net, mon
# ---------------- VISUALIZATION ---------------- #
def plot_firing_rate_disto(idxs, ts, ax, name):
"""plots distribution of firing rates over the simulation"""
T = np.max(ts) - np.min(ts)
_, rates = np.unique(idxs, return_counts=True)
rates = rates * 1.0 / T
ax.hist(
rates,
bins=25,
density=True,
label=name,
histtype="step",
orientation="horizontal",
lw=2,
)
ax.set(
ylabel="Firing rate [Hz]",
xlabel="Probability density",
xscale="log",
ylim=(0, 64),
)
def plot_in_deg(in_deg, ax, ax_hist, name):
"""plots distribution as well as the heat map of in-degree from each neuron."""
# field map & distribution of in-degrees
m = ax.pcolormesh(in_deg, shading="flat", vmin=0.5 * NCONN, vmax=1.5 * NCONN)
ax_hist.hist(
in_deg.flatten(),
bins=50,
density=True,
label=name,
histtype="step",
orientation="horizontal",
lw=2,
)
ax_hist.set(ylabel="In-degree", ylim=(0.5 * NCONN, 1.5 * NCONN))
ax.set(
aspect="equal",
xticks=[],
yticks=[],
title=name,
)
ax_hist.locator_params(axis="x", nbins=3)
return m
def animator(fig, all_imgs, all_vals):
"""used for making an activity animation"""
n_frames = len(all_vals[0][0]) # total number of frames
def animate(frame_id):
for img, vals in zip(all_imgs, all_vals):
img.set_array(vals[frame_id])
return all_imgs
# Call the animator.
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(
fig, animate, frames=n_frames, interval=50, blit=True
)
return anim
def plot_animations(all_idxs, all_ts, duration, fig, axs, cax, ss_dur=25):
"""Plots neuronal activity as an animation"""
ts_bins = np.arange(0, duration / ms + 1, ss_dur) * ms
field_vals, field_imgs = [], []
for idxs, ts, ax in zip(all_idxs, all_ts, axs.flat):
h = np.histogram2d(ts, idxs, bins=[ts_bins, range(GRID_SIZE**2 + 1)])[0]
field_val = h.reshape(-1, GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE) / (float(ss_dur * ms))
field_img = ax.imshow(field_val[0], vmin=0, vmax=64, origin="lower")
field_imgs.append(field_img)
field_vals.append(field_val)
ax.set(xticks=[], yticks=[])
plt.colorbar(field_img, cax=cax)
anim = animator(fig, field_imgs, field_vals)
return anim
# ---------------- MAIN ---------------- #
fig, axs = plt.subplots(
2,
6,
figsize=(15, 6),
layout="constrained",
gridspec_kw={"width_ratios": [1, 1, 1, 1, 0.1, 1]},
)
all_idxs, all_ts = [], []
for idx, lscp in enumerate(["symmetric", "random", "perlin", "homog"]):
print(f"Simulating {lscp} landscape.")
phis = landscape(lscp)
net, mon = simulate(phis)
## Static plots
# In-degrees
syn = net["syn_II"]
in_deg = syn.N_incoming_post.reshape((GRID_SIZE, GRID_SIZE))
m = plot_in_deg(in_deg, axs[0, idx], axs[0, 5], lscp)
# Firing rates
idxs, ts = mon.it
all_idxs.append(idxs)
all_ts.append(ts)
plot_firing_rate_disto(idxs, ts, axs[1, 5], lscp)
# Add colorbar and legend for in-degree plots
plt.colorbar(m, cax=axs[0, 4])
axs[0, -1].legend()
# Plot animations
duration = net.t
anim = plot_animations(all_idxs, all_ts, duration, fig, axs[1, :4], axs[1, 4], ss_dur=25)
plt.show()